On January 5th, the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) officially kicked off. One of the key highlights of the event was Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang’s keynote speech, which provided insights into the AI revolution, industry trends, and Nvidia’s latest product and technological innovations. This article will discuss these developments from three perspectives: core trends, business highlights, and future outlook, offering a comprehensive review of the current state of the AI industry.
If you would like to know more about Nvidia’s business segments, you can also read US Industry 101: Introduction to Nvidia Business Segments
Core Trends
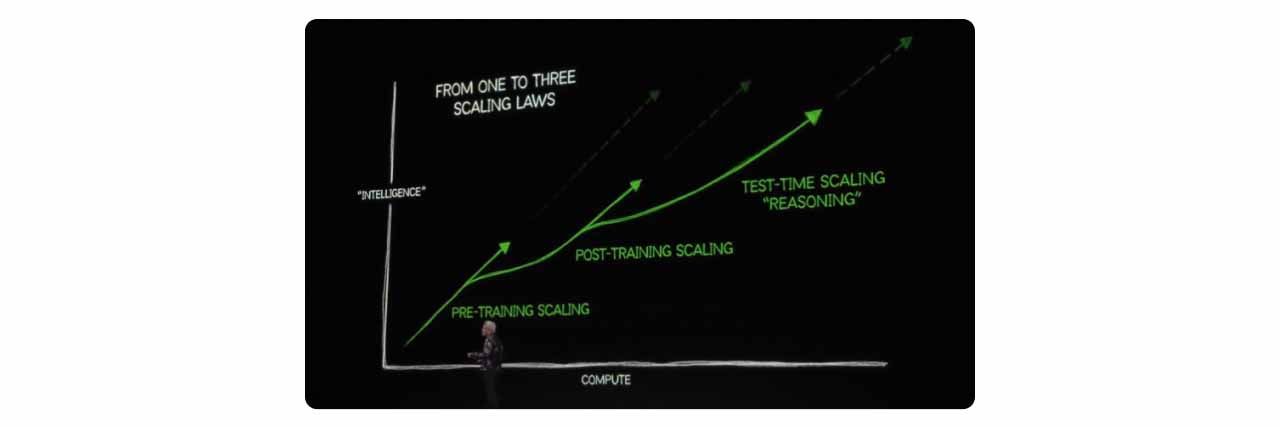
AI models were originally improved through the Scaling Laws, which emphasized expanding data volume and model size to enhance performance and accuracy. Huang pointed out that the focus has now shifted to Post-Training Scaling and Test-Time Scaling, enabling AI models to analyze data quality and problem complexity beforehand, while also refining responses based on user feedback. This evolution demands even greater GPU computational power, reinforcing the increasing need for high-performance GPUs.
The rapid advancement of GPU-driven AI computing has pushed AI beyond Perception AI (recognizing patterns) and Generative AI (creating content), leading to Agentic AI, where AI can reason, plan, and take actions. The next evolution, Physical AI, will allow AI to interact with the physical world, assisting humans in real-world tasks.
AI is also expanding beyond cloud computing, gradually integrating into PCs, software, and digital assistants. The next breakthrough will be its application in enterprise solutions, autonomous vehicles, and robotics—bringing AI from the virtual world into real-world industries.
"GeForce brought AI to the world, democratized AI. Now, AI has come back and revolutionized GeForce." — Jensen Huang
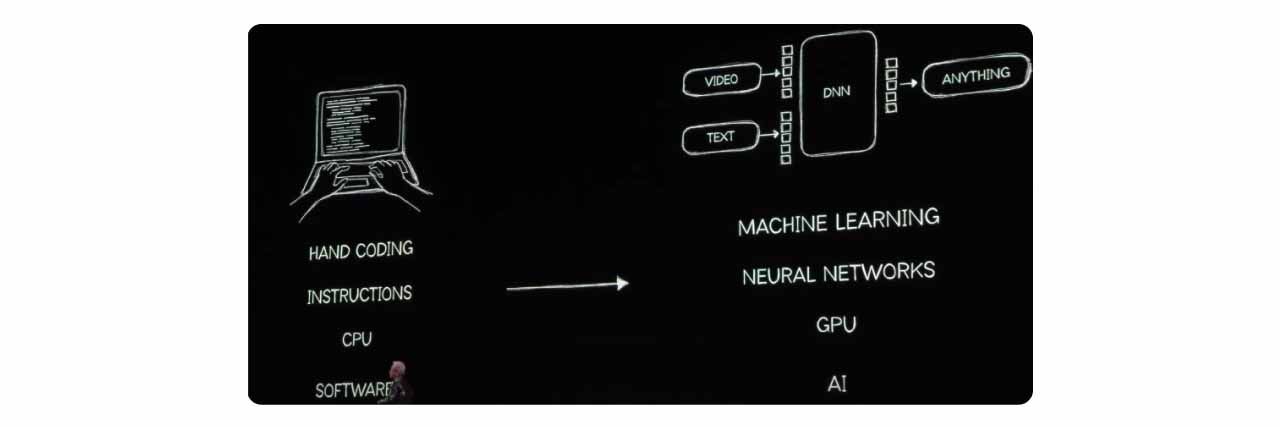
Jensen Huang discussing machine learning: Traditional software development vs. the future of AI-powered software.
Huang emphasized that AI and GPUs now drive each other’s advancement, creating a positive feedback loop that fuels innovation across industries.
Another key focus was machine learning, which enhances AI models by processing vast amounts of data through deep neural networks (DNNs). Traditional software development required manual coding, instructing CPUs to execute specific tasks. Now, machine learning enables applications to self-improve through AI-driven learning, making interactions with AI as intuitive as consulting an expert.
This not only reduces costs for enterprises but also optimizes resource utilization and boosts efficiency. Huang’s emphasis on AI training and machine learning automation was evident in Nvidia’s product demonstrations.
Key Business Highlights
Highlight 1: GeForce RTX
Gaming has been the foundational business of Nvidia, with the GeForce RTX series serving as its flagship product. This lineup emphasizes real-time ray tracing, delivering highly realistic visual effects. RTX renders light rays for each pixel, and with AI integration, it not only reduces computational workload by predicting most pixels but also enhances frame rates while maintaining image clarity. This technology is known as Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS).
To support these advancements, GPUs must be powerful enough to handle the processing demands. Therefore, Jensen Huang also announced the next-generation RTX Blackwell architecture. The new design features 92 billion transistors and exceeds 4000 Trillions of Operations Per Second (TOPS) in computational power. Beyond basic graphics rendering, it integrates neural networks, enabling breakthrough computational performance on top of its already extensive processing capabilities.
The RTX 4090 is currently the fastest GPU in the world, priced at $1,599. However, Jensen Huang revealed that, with AI optimization, Nvidia was able to reduce GPU processing load, leading to the development of the RTX 5070. This new model delivers the same performance as the RTX 4090 but at a significantly lower price of $549, showcasing AI’s potential in optimizing GPU efficiency.
Additionally, Nvidia announced the RTX 5070 Ti, 5080, 5090, and an ultra-thin RTX 5070 laptop GPU (only 14.9mm thick), with mass shipments expected in January. The RTX 5090 delivers twice the performance of the RTX 4090, and upon release, it will replace the RTX 4090 as the world’s fastest GPU.
Highlight 2: Nvidia Cosmos & Robotics
ChatGPT's model is language-oriented, designed to understand textual context and communicate with humans. Similarly, for Physical AI to integrate into the real world, it must first understand the fundamental principles of how the world operates. One key challenge AI currently faces is the lack of human intuition. To address this, Jensen Huang introduced Nvidia Cosmos, a model that equips AI with fundamental physical knowledge—such as gravity, friction, and other natural forces—allowing AI to evaluate user commands within a real-world context. With this foundational understanding, AI can assist humans in performing actions that align with physical reality. Nvidia Cosmos is now available on GitHub.
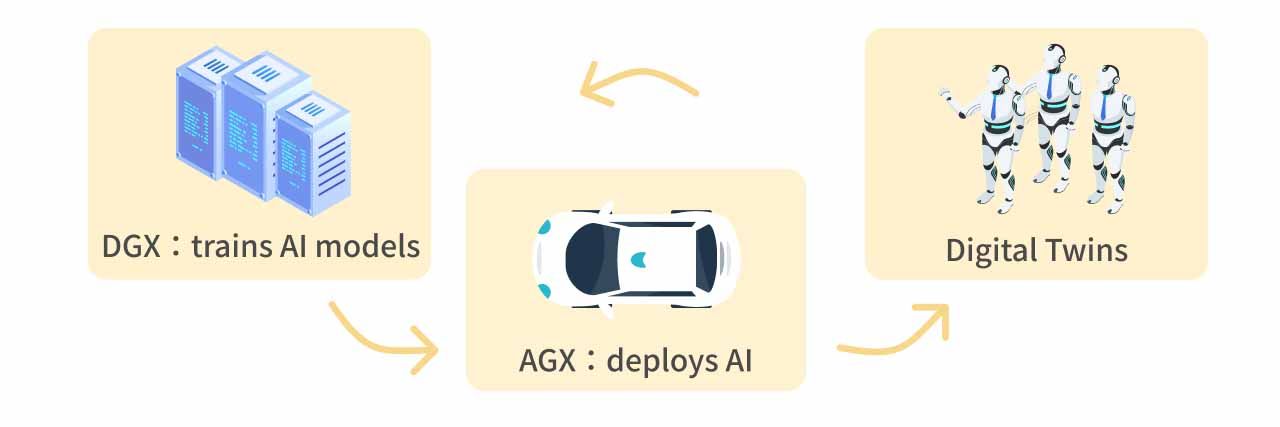
Huang further stated that, in the future, every company will utilize three computing systems to establish a foundational framework for industrial robotics applications. This framework consists of three key components:
- DGX, which trains AI models.
- AGX, which deploys AI in real-world environments.
- Digital twins, formed by Cosmos and Omniverse, which provide simulation environments.
By combining Cosmos' physical world knowledge with Omniverse's virtual space, digital twins enable AI to simulate real-world scenarios, gather training data, and acquire experience efficiently. These three elements are interconnected and essential, forming a critical foundation for expanding the applications of Physical AI. In the future, this framework will play a key role in autonomous vehicles, robotics, and industrial automation, helping AI transition from virtual models to real-world execution.
Highlight 3: Autonomous Vehicles

Nvidia has partnered with Toyota and other automakers to jointly develop autonomous vehicles. Jensen Huang also showcased Thor, Nvidia’s next-generation automotive processor, which is built on the Blackwell architecture and delivers 20 times the computing power of its predecessor, Orin. Thor is currently in full-scale production.
At present, Nvidia’s Drive OS has obtained ASIL-D certification (Automotive Safety Integrity Level D), the highest safety certification level for automotive systems. Moving forward, Nvidia will continue integrating real-world driving data and digital twin simulations to enhance the adaptability of autonomous vehicles in complex driving scenarios.
Nvidia’s autonomous vehicle business has already reached $4 billion in revenue. Huang stated that by 2025, revenue from electric vehicle (EV) computing is expected to surpass $5 billion. He also emphasized that autonomous vehicles will be the first trillion-dollar robotics industry, making it a key development focus for Nvidia.
Highlight 4: Project Digits
The Deep Learning GPU Intelligence Training System has also been a major highlight. In 2016, Nvidia introduced its first deep learning supercomputer, DGX-1, providing researchers and startups with a plug-and-play supercomputing system for AI training. This eliminated the need for companies to invest significant costs and resources in building their own infrastructure. However, as the AI boom continues, the scope and demand for AI applications have grown exponentially.
Jensen Huang announced that Nvidia has miniaturized its DGX system, integrating all its AI technologies into a compact AI supercomputer. This new system, called Project Digits, consolidates development, deployment, and execution into a single unit, offering researchers a more efficient and cost-effective AI testing platform.
Notably, Huang specifically mentioned that the super CPU in Project Digits was co-developed by Nvidia and MediaTek, utilizing MediaTek's SoC (System-on-Chip) technology. This processor is already in production and is expected to launch in May.
Future Outlook
This business showcase centered on enhancing AI’s depth of reasoning as a core technology, with robotics serving as a crucial means to realize AI’s vision. The goal is to improve AI performance and gradually lead AI into real-world applications, a concept known as Edge AI. Innovations in edge computing will accelerate the development of Industry 5.0, reshape daily life, and expand AI’s applications across various domains. At its core, continuously broadening AI’s scope remains Nvidia’s key objective, driving both the company and the AI industry toward new heights.
When discussing robot training, Jensen Huang emphasized that a fundamental challenge in AI development is “how to train robots.” This involves not only increasing computing power but also improving training methodologies, feedback mechanisms, and large-scale data collection. The greatest challenge in advancing AI capabilities depends on Nvidia’s ability to innovate, as it serves as a driving force in the AI industry. Whether Nvidia’s technology can keep pace with Huang’s vision for the AI sector will play a crucial role in shaping AI’s future trajectory.
For investors, Nvidia’s ongoing innovations and breakthroughs in these areas will be key factors to watch in the company’s growth and impact on the broader AI industry.
If you are also interested in AI related industry, you could also read: News Feature: OpenAI’s Transition Towards Profitability
