In 1993, NVIDIA was founded by current CEO Jensen Huang and his friends, introducing the world to the GPU in 1999—a groundbreaking invention in computer graphics. As AI rapidly ascended in 2023, NVIDIA surged in popularity, becoming a central topic of discussion. As an industry leader, NVIDIA’s moves are closely tied to AI innovation, with many companies across the supply chain reaching new commercial heights alongside NVIDIA. But what exactly does NVIDIA do, and why is it attracting such global attention? Below we will introduce some of the biggest business segments in Nvidia.
Business Segment Breakdown
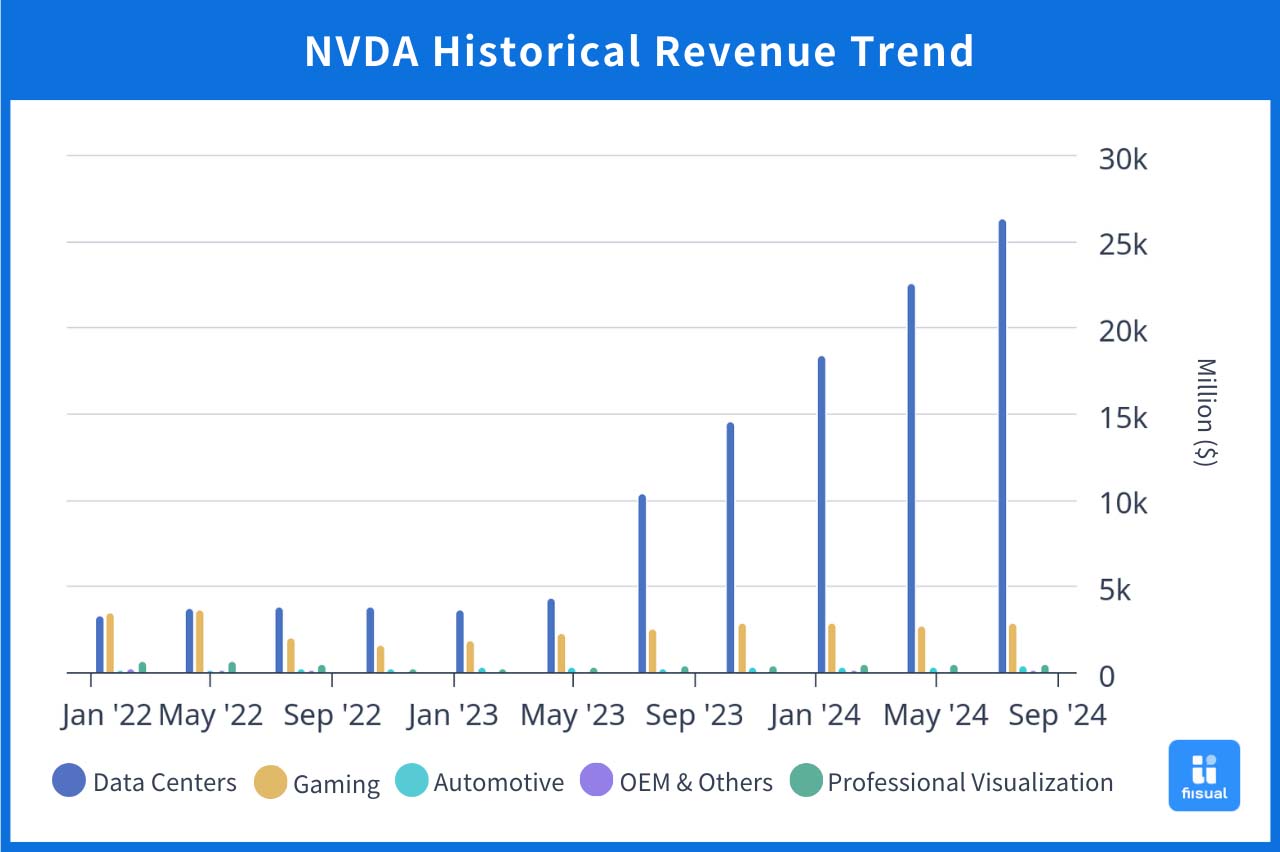
Graph: Historical Revenue Trends for NVIDIA’s Business Segments.
Over the past decade, NVIDIA’s revenue has primarily come from its gaming segment, with gaming graphics cards as a key product. However, due to the digital transformation driven by the 2021 pandemic, data demand surged, positioning the Data Center segment as the largest revenue contributor. As generative AI services such as ChatGPT emerged at the end of 2022, the future AI applications became clear, and many companies began investing heavily in AI development, driving up demand for GPUs. This AI boom led to rapid revenue growth from 2023 Q2, with the data center segment’s share overshadowing other segments.
Segment One: Data Centers

Data centers have become NVIDIA’s primary revenue source, accounting for about 87% of total revenue, and are among its most vital divisions. This segment consists of computing and networking, offering customers products in modular system formats. NVIDIA’s unparalleled status is due to its data center’s focus on accelerated computing, enhancing processing efficiency. NVIDIA’s robust integration of hardware, software, and programming systems provides comprehensive computing solutions, allowing developers to harness these systems effectively and efficiently. Clients include major public and private sector entities, with NVIDIA helping them build and operate data centers.
Computing Segment
The computing segment of the data center provides hardware solutions such as GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) and DPUs (Data Processing Units), supplying processing power for end customers. The segment is also responsible for building supercomputing platforms by integrating hardware, software, and tools for efficiently processing large-scale computations. As the leader in AI computing chips, NVIDIA’s computing segment faces the challenge of staying ahead in this rapidly advancing field. A fabless semiconductor company, NVIDIA partners with TSMC and others for chip manufacturing, focusing on R&D and sales to accelerate chip iteration.
A recent product capturing market attention is the GB200, a super chip based on the Blackwell architecture, comprising the B200 and Grace CPU. Set for Q4 release, it promises breakthroughs for AI development. NVIDIA plans to ramp up production through FY2026, potentially reaping billions in revenue. With computing accounting for over two-thirds of total revenue, AI-driven growth is expected to continue fueling demand for hardware solutions.
Networking Segment
As NVIDIA’s chip capabilities progress, the networking segment must continuously enhance data I/O performance for GPUs to fully leverage their processing speeds, improving system efficiency and adaptability. NVIDIA’s acquisition of Mellanox for $7 billion in 2020 highlighted its focus on advanced networking technologies to tackle data center transmission issues. NVIDIA now provides accelerated networking solutions with InfiniBand and Ethernet to meet computational demands. InfiniBand supports high-speed, low-latency applications like supercomputing and large data centers, while Ethernet suits data center and enterprise environments.
Segment Two: Gaming

Gaming graphics cards have long been a core NVIDIA product. With a market share exceeding 80%, NVIDIA offers a range of products for various gamers, from entry-level to professional, providing noticeable improvements in performance and gaming experience with each generation.
The GeForce line remains its flagship gaming series, with the GeForce RTX series focusing on real-time ray tracing for realistic visual effects. Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) technology leverages AI to produce clearer images at high frame rates. Recently popular games like Black Myth: Wukong in China and Taiwan have used the RTX and DLSS technology to deliver highly immersive visuals. Although the gaming segment’s revenue share has decreased, NVIDIA’s continued innovation and dominance ensure its stability in the future.
Segment Three: Professional Visualization

NVIDIA’s professional visualization technology assists various fields, whether enhancing visual effects for designers or managing factory operations. For digital content creation, it offers sharper, more precise effects; for enterprises, 3D and simulation technologies can help digitalize manufacturing processes. NVIDIA also partners with independent software vendors (ISVs) to integrate its technology into professional workflows like medical imaging for greater efficiency.
The Quadro line was previously a staple in this segment but has been rebranded under the RTX name, emphasizing ray tracing advantages for 3D modeling and engineering design applications. The Omniverse platform integrates NVIDIA’s hardware and software to support simulations and collaboration, providing a concrete framework for the metaverse concept. With its extensive customization options for various enterprises, the professional visualization segment holds significant growth potential.
Segment Four: Automotive
NVIDIA has consistently developed solutions for the automotive market, providing autonomous driving technology and solutions that are widely applied in automotive contexts. Its unique end-to-end solutions allow vehicles to improve performance over time through updates, extending their useful life.
Products include DRIVE Orin chips and the DRIVE OS operating system. The NVIDIA DRIVE AGX platform combines hardware and software for large-scale autonomous driving development. NVIDIA’s automotive partners include major global brands like Mercedes-Benz and Volvo, which aim to integrate AI into vehicles. A new Dimensity automotive platform was recently launched in collaboration with MediaTek, featuring the CT-X1 cabin system, equipped with a powerful 3nm automotive chip.
Although global electric vehicle sales have slowed, advancements in automotive technology are ongoing. This segment is still in its early stages, representing a small portion of NVIDIA’s revenue, but has the potential to grow into a significant income source as it matures.
Segment Five: OEM & Others
NVIDIA also supplies GPUs to PC manufacturers like Dell and HP, enabling them to incorporate NVIDIA chips into their products. Additionally, NVIDIA licenses designs and technologies to support product development for these companies. Although revenue here is relatively modest, partnerships with NVIDIA add value and innovation to various manufacturers’ product lines.
Summary
Hope you have a clearer understanding of NVIDIA’s business after reading this article. NVIDIA’s scope is broad, spanning AI and beyond, leveraging its GPUs’ powerful performance across diverse sectors. Investors may find it helpful to monitor the many fields NVIDIA touches, as new industry trends could emerge along the way!
For people who are interested in AI related industry, you can also refer to the following articles.
Taiwan Industry 101: Introduction to CoWoS Technology
