With the rapid advancement of technology, having a smartphone has become the norm. Among the many smartphone brands, iPhone remains the top choice for consumers today. From computers to iPhones, and from hardware products to innovative software services, Apple's presence is everywhere. Not only has it transformed user experiences, but it has also reshaped the entire industry landscape. Below we will be diving in and explore the details about Apple!
Company Overview
“To bring the best user experience to customers through innovative hardware, software, and services.” — Apple’s mission statement
Apple Inc. (AAPL), founded by Steve Jobs in 1976, is a company focused on designing and manufacturing mobile communication devices and providing software services. Its product lineup includes popular hardware such as the iPhone, iPad, and AirPods, as well as software services like iCloud and Apple Music, along with operating systems such as iOS and macOS. In 2007, Apple introduced the revolutionary iPhone, an all-in-one device that fundamentally changed the way people use mobile phones worldwide. This innovation propelled Apple to global fame, making it one of the most influential tech giants. As of December 2024, Apple’s market capitalization has reached $3.7 trillion, making it the most valuable company in the world.
Business Model

Simply just an iPhone consists of more than 200 different components, which demonstrates the massive scale of Apple’s supply chain. This has driven significant growth not only in Taiwan’s tech sector but also across the global supply chain, creating the phenomenon of "Apple concept stocks." To manage costs and mitigate manufacturing risks, Apple adopts a diversified supplier strategy. This approach gives Apple greater bargaining power and control, allowing it to maintain a long-term hardware gross margin of 35–40%. Despite the complexity of its components and highly diversified business operations, Apple adheres to two core principles: "core technologies" and "key components." Apple focuses its resources on product development and the production of critical technologies, while outsourcing other manufacturing processes, ensuring an efficient division of labor.
Apple’s sales strategy is another key factor behind its strong business model. The company has developed multiple sales channels, including third-party retailers, distributors, and its own online and physical Apple Stores. While third-party retailers follow standard sales processes, Apple’s direct-to-consumer channels—both online and in-store—are designed to enhance customer experience through visual and interactive engagement, reinforcing its brand values. This strategy not only strengthens the connection between Apple and its customers but also enhances brand loyalty.

Apple’s ecosystem seamlessly integrates its vast range of hardware and software services, creating a powerful closed-loop system. Additionally, Apple places a strong emphasis on user privacy, an aspect that has gained increasing importance in today’s digital world, earning widespread consumer trust. These strategies have driven high user preference for Apple products and cultivated a massive global fanbase. Currently, the iPhone holds over 25% of the global smartphone market, and in the U.S., its market share exceeds 55%, solidifying Apple’s leadership in the industry.
Apple’s Business Segments
According to Apple’s latest Q4 2024 financial report, the revenue breakdown is as follows:
| Q4 2024 (Billion USD) | YoY (%) | Revenue Share (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| iPhone | 46.22 | +5.52 | 48.69 |
| Services | 24.97 | +11.91 | 26.31 |
| Other Products | 9.04 | -3 | 9.52 |
| Mac | 7.74 | +1.7 | 8.16 |
| iPad | 6.95 | +7.87 | 7.32 |
| Total Revenue | 94.93 | +6.07 | 100 |
Apple’s business spans multiple categories, with revenue streams divided into five key segments: iPhone, Mac, iPad, Other Products (including AirPods and HomePod), and Services. While the iPhone’s share of revenue has gradually declined, it remains Apple’s largest income source. The high-margin Services segment, with a gross margin exceeding 70%, continues to grow, helping Apple boost its overall gross margin from 40% to 45%. Below is an overview of Apple’s major business units and product lines:
Segment 1: iPhone
Smartphones have always been Apple’s primary revenue driver, with each new iPhone launch generating significant consumer interest. Apple typically unveils new iPhones in September, aligning with year-end upgrade trends. This year, the iPhone 16 introduced new features such as a dedicated camera control button and Apple Intelligence, an AI-powered enhancement that improves user experience.
Segment 2: Software Services
This segment includes the App Store, Apple Music, iCloud subscriptions, AppleCare, Apple Pay, and more. CEO Tim Cook noted in the latest earnings call that the strong growth in services is driven by stable demand for device sales and paid subscriptions. After an initial period of slow adoption, Apple’s software services have now achieved a "flywheel effect," steadily increasing revenue. According to estimates from U.S. research firm Trefis, the App Store accounts for 30% of Apple’s Services revenue. Additionally, Google pays Apple significant licensing fees to be the default search engine on Safari. However, an ongoing U.S. antitrust lawsuit may force Apple to separate Safari’s default search engine from Google, potentially reducing Apple’s Services revenue by 20%.
Segment 3: Other Products – Vision Pro

Apple’s Vision Pro, launched in early 2024, marks its entry into a new product category beyond smartphones and laptops. Positioned as an AR/VR device (primarily AR-focused), it features M2+R1 chips and dual micro-OLED displays, delivering high computational power and visual clarity. Vision Pro serves as a virtual workspace, integrating seamlessly with Apple’s ecosystem for multitasking. However, due to high pricing, unclear market positioning, and limited standout features, sales have fallen short of expectations. Recent reports suggest Apple may discontinue the current model and release a more affordable version in the future.
Future Outlook & Risks

Apple’s main hardware competitors include Samsung in smartphones and Dell/Lenovo in laptops, while its software rivals include Google and Microsoft. However, unlike hardware firms that rely on Android and Windows or software firms that lack competitive hardware, Apple stands out with its fully integrated ecosystem. Apple’s high system compatibility and ability to rapidly develop tailored solutions make it difficult for competitors to match its ecosystem integration. However, its closed system also presents risks. Developers must rely heavily on Apple’s platform, leading to lower flexibility, while businesses dependent on Apple for distribution face Apple’s strong bargaining power. These factors have led to increasing antitrust scrutiny worldwide.
To better understand Apple’s future possible risks and development, we can divide into two main sectors:
Risk: Slowing iPhone Upgrade Cycle
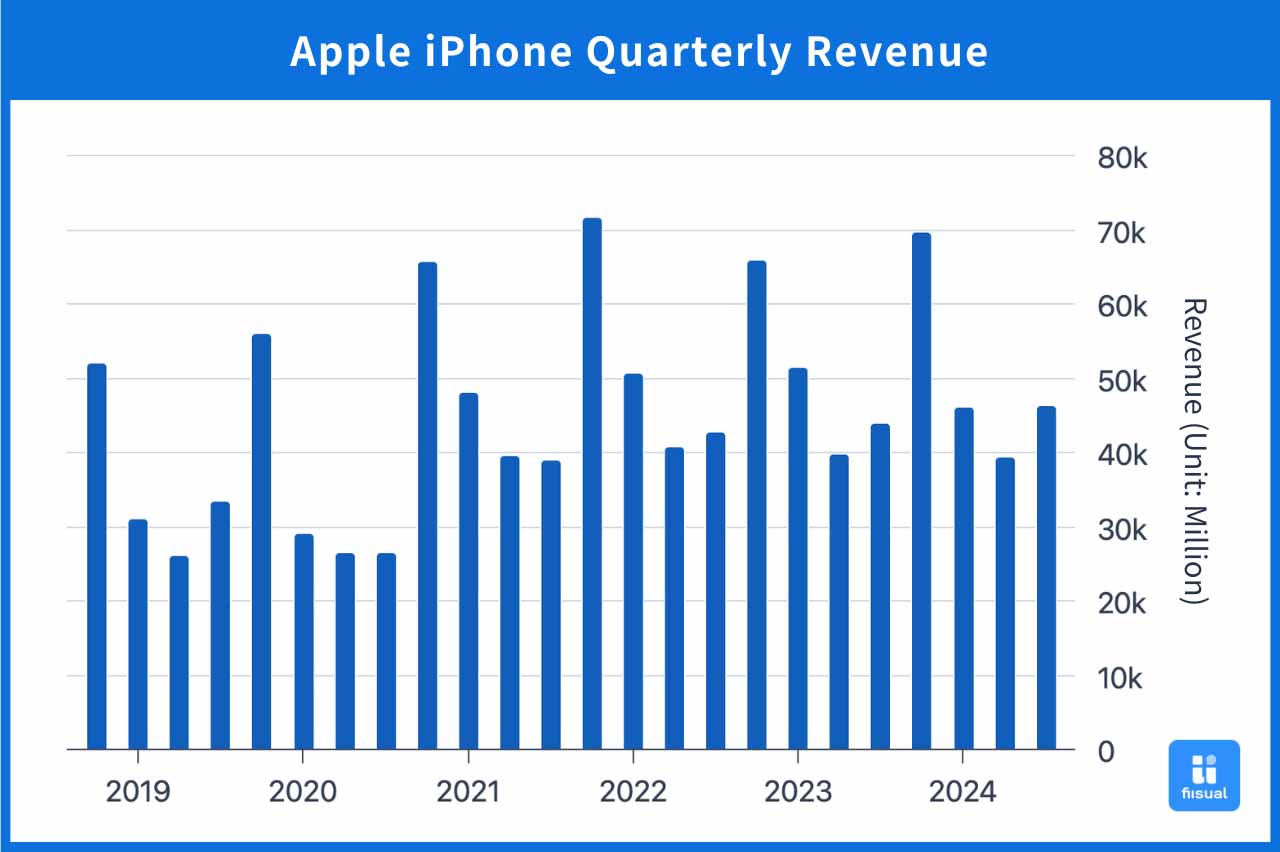
The price increase of iPhones has been slowing down in recent years, and the iPhone 16 has unexpectedly maintained the same price as the iPhone 15. However, Apple's revenue over the past three years shows that iPhone earnings have been gradually slowing, raising concerns among investors and reflecting a decline in sales volume and weaker consumer demand for upgrades.
In today's highly competitive smartphone market, Apple's ability to stay ahead depends on whether innovation can drive upgrade demand. Taking the launch of the iPhone 16 as an example, market response and discussions have been relatively muted, and its AI applications were largely within public expectations. As a result, revenue growth in the next quarter is unlikely to see a significant boost. Apple’s executives also stated in the latest financial report that they may not achieve double-digit annual growth as previously anticipated.
Opportunity: AI & AR Innovation
To mitigate the competitive risks in the consumer electronics market, Apple has recently focused on technological innovation and the development of new business ventures. Following the trend set by tech giants like Meta and Google, Apple has expanded its efforts in AI and wearable devices, launching its new AI technology—Apple Intelligence—and the mixed reality (MR) headset, Vision Pro, this year.
However, as Apple entered these fields relatively late, its current performance has yet to meet market expectations, raising concerns among investors. Despite this, Apple's executives remain confident in the long-term potential of both technologies, believing they offer vast application opportunities. Additionally, Apple appears to be leveraging Apple Intelligence to enhance the functionality of its product ecosystem, suggesting that more breakthroughs and innovations can be expected in the future.
