When people hear about the term "goodwill," they often associate it with a company’s reputation or trustworthiness. However, in accounting, its definition is entirely different!
In financial statement analysis, goodwill on the balance sheet is often overlooked. However, during mergers and acquisitions (M&A), goodwill is a crucial indicator of corporate value. It not only represents a company’s intangible assets but also reflects the acquiring firm's recognition of the target company’s brand, customer relationships, and market position. Moreover, goodwill signifies a company’s competitive strength and future growth potential, making it an essential factor in financial analysis.
In today’s article, let’s explore this indispensable component of M&A, breaking down its definition, calculation, and impact on financial analysis to uncover its true significance!
We also covered the concept of goodwill in our article Financial Report 101: Introduction to the Balance Sheet
What Is Goodwill?
The word “goodwill” in English typically implies kindness or positive intent. However, in accounting, goodwill is a technical term that represents the excess value of a company beyond its tangible assets and liabilities. It is classified as an intangible asset on the balance sheet.
How Is Goodwill Calculated?
Goodwill = Purchase Price – Fair Value of Net Assets Acquired
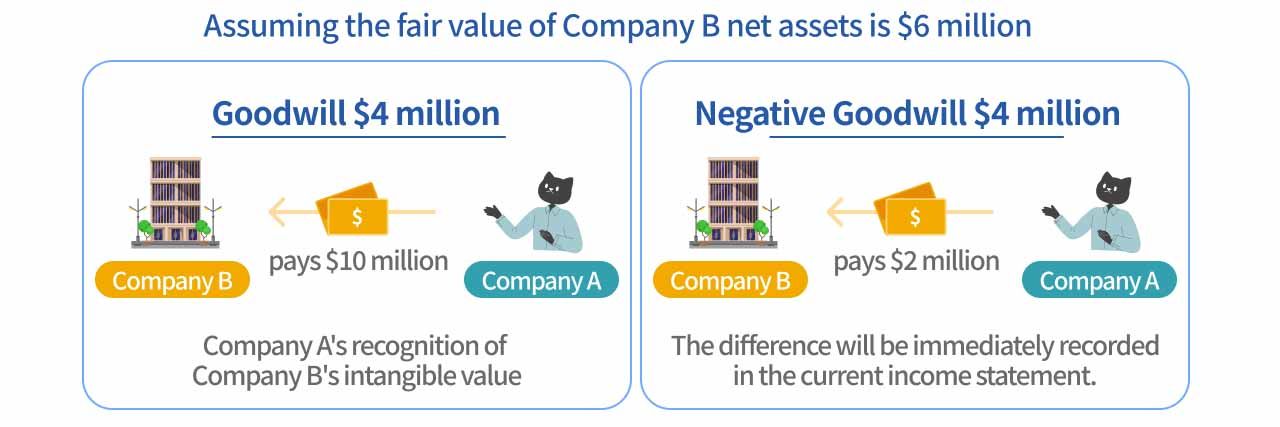
For Example: Company A, a large tech firm, decides to acquire Company B, an AI-focused company. The fair value of Company B’s net assets (total assets minus liabilities) is $6 million, but Company A is willing to pay $10 million for the acquisition. The $4 million premium represents the value Company A sees in B’s technology, patents, and market potential—this amount is recorded as goodwill.
However, if Company B fails to meet performance expectations post-acquisition, such as failing to achieve technological breakthroughs or losing market share, Company A may need to write down goodwill through an impairment process.
The Core Meaning of Goodwill
Goodwill only arises from M&A transactions and represents the premium paid over the fair value of net assets. This reflects the acquiring company's recognition of the target’s brand value, market position, customer base, and proprietary technology.
What Is Negative Goodwill?
If the purchase price is lower than the fair value of net assets, negative goodwill occurs, also known as a "bargain purchase gain." In accounting, this difference is immediately recorded as income in the profit and loss statement, reflecting that the acquirer obtained the target company’s assets at a discount.
Goodwill vs. Other Intangible Assets
| Goodwill | Other Intangible Assets | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Goodwill represents the premium paid in M&A for a company’s intangible value, such as brand recognition and customer relationships. It cannot be independently identified or sold. | Intangible assets such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights are created, purchased, or registered by the company. They can be independently valued and traded. |
| Lifespan | Goodwill has no specific lifespan or standalone valuation. | Other intangible assets typically have a defined acquisition cost and useful life. |
| Amortization | Goodwill cannot be amortized but must undergo annual impairment testing to check if its book value exceeds its actual value. If impaired, the loss is recorded in the income statement. | Most other intangible assets are amortized over time, spreading the cost across accounting periods. |
While goodwill is classified as an intangible asset, it is treated separately from other intangible assets in financial reporting. In countries like the U.S., goodwill is listed as a distinct item on the balance sheet, reflecting its unique nature and impairment treatment.
In contrast, Taiwan includes goodwill under intangible assets, which reflects differences in accounting standards and M&A activity levels. Given Taiwan’s dominance in small-to-medium enterprises and manufacturing, M&A deals often focus on physical assets (e.g., land, machinery) rather than brand value or market position. This results in lower goodwill recognition in Taiwan’s financial statements. However, in countries with technology-driven industries (e.g., U.S., Europe, healthcare, and AI sectors), goodwill plays a much larger role, necessitating separate reporting for financial analysis.
Impact of Goodwill on Financial Statements
| At Acquisition | After Impairment | |
|---|---|---|
| Balance Sheet | Goodwill is recorded as a non-current asset under intangible assets. | If impaired, goodwill is reduced, total assets decrease, and shareholders' equity is affected. |
| Income Statement | Goodwill is not initially recorded as an expense. | Impairment losses are recognized under non-operating expenses, reducing net profit. |
| Cash Flow Statement | The purchase price is recorded under cash outflows from investing activities, reflecting the acquisition cost. | Impairment does not involve actual cash outflows but is added back in operating cash flow adjustments. |
Case Study: Facebook’s Acquisition of Instagram
Facebook Buy Instagram? In 2012, Facebook (now Meta) acquired Instagram for $1 billion, despite the company being less than 18 months old at the time. By 2010, Instagram had 30 million users, experiencing explosive growth. Its mobile-first photo-sharing model attracted younger audiences, complementing Facebook’s aging user base. Facebook’s acquisition strengthened its dominance in social media by securing a fast-growing competitor. By 2018, Instagram reached 1 billion users and became one of Meta’s most valuable platforms, driving substantial advertising revenue growth. This acquisition solidified Facebook’s leadership in the social media industry and is now seen as one of the most strategic M&A deals in tech history.
How Was Goodwill Recognized in Facebook’s Financials?
During the $1 billion acquisition, the fair value of Instagram’s tangible assets and liabilities was significantly lower than the purchase price. The excess amount was recorded as goodwill in Facebook’s balance sheet as non-current assets.
What Did This Mean on the Balance Sheet?
If the estimated figures are accurate, Facebook likely paid a premium of over $50 million for the acquisition, indicating that Instagram’s goodwill value exceeded $50 million, surpassing its tangible asset value.
This goodwill not only reflects Facebook’s commitment to the acquisition but also signifies its recognition of Instagram’s brand value, user base, and future growth potential. Moreover, it demonstrates Facebook’s confidence that integrating Instagram would enhance market influence and profitability.
How Could This Goodwill Be Reduced?
According to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), goodwill is not amortized but is instead adjusted through annual impairment testing.
If Instagram underperforms in a given year, causing its valuation to drop to $500 million while its goodwill book value remains at $700 million, an impairment loss of $200 million must be recognized in the income statement for that year.
Conclusion: Why Goodwill Matters
Goodwill plays several critical roles in corporate finance:
- Bridging Valuation in M&A – Helps acquirers assess the target’s long-term value, guiding strategic acquisition decisions.
- Indicator of Competitive Strength – Reflects a company’s brand, customer base, and technological assets, reinforcing its market position.
- Risk Management Signal – Requires annual impairment testing, serving as a key indicator of financial health. A significant write-down can alert investors and management to potential risks.
Understanding goodwill is essential for M&A analysis, financial forecasting, and corporate strategy, making it a crucial metric in evaluating a company's true market value.
