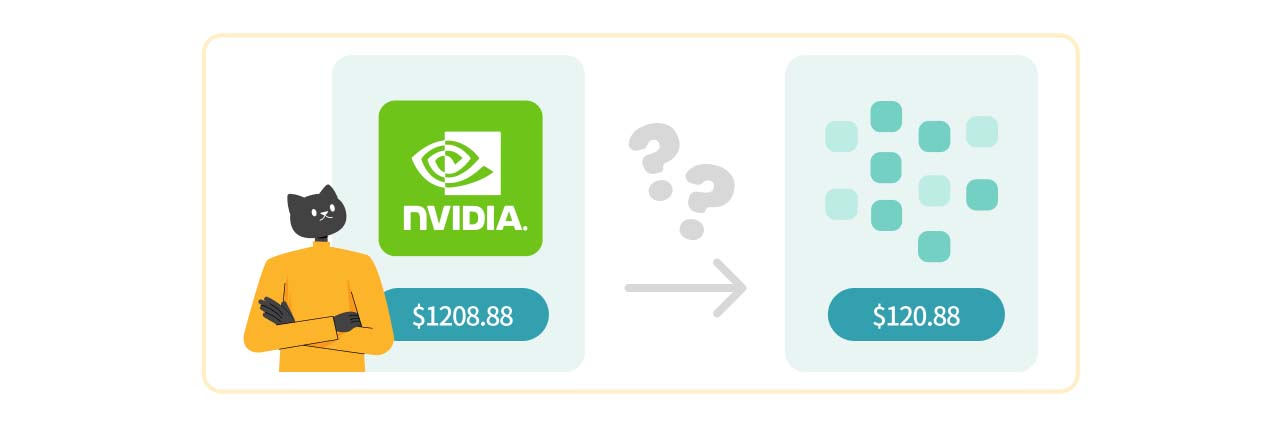
Nvidia's 1-for-10 stock split officially took effect on June 10, 2024, with the share price adjusted from its closing value of $1,208.88 to $120.88. This reduction in price is expected to attract more investors, with many on social media exclaiming, "Nvidia (NVDA) just got cheaper!"
Below we will be explaining what a stock split is.
What is a Stock Split?

A Stock Split is a Way to Restructure Shares
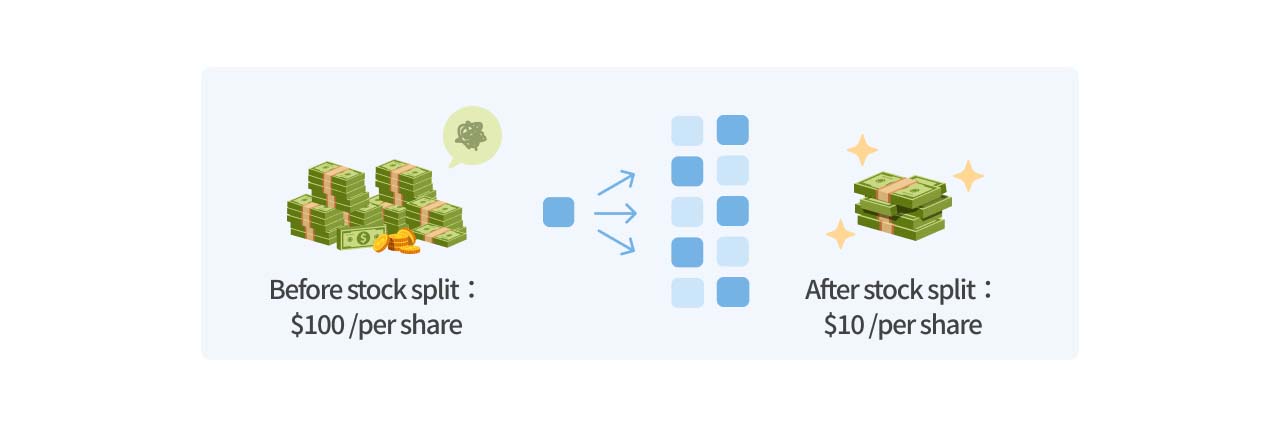
A stock split is a method by which a company restructures its shares, adjusting the price per share in proportion to the split, without impacting the shareholders' total equity. In simple terms, a common stock split, such as Nvidia's 1-for-10 plan, means that a shareholder who originally held 1 share will now own an additional 9 shares, for a total of 10 shares. The share price will then be adjusted to 1/10 of the original price. Thus, the total value of the original shareholder’s holdings remains unchanged after the split.
Types of Stock Splits
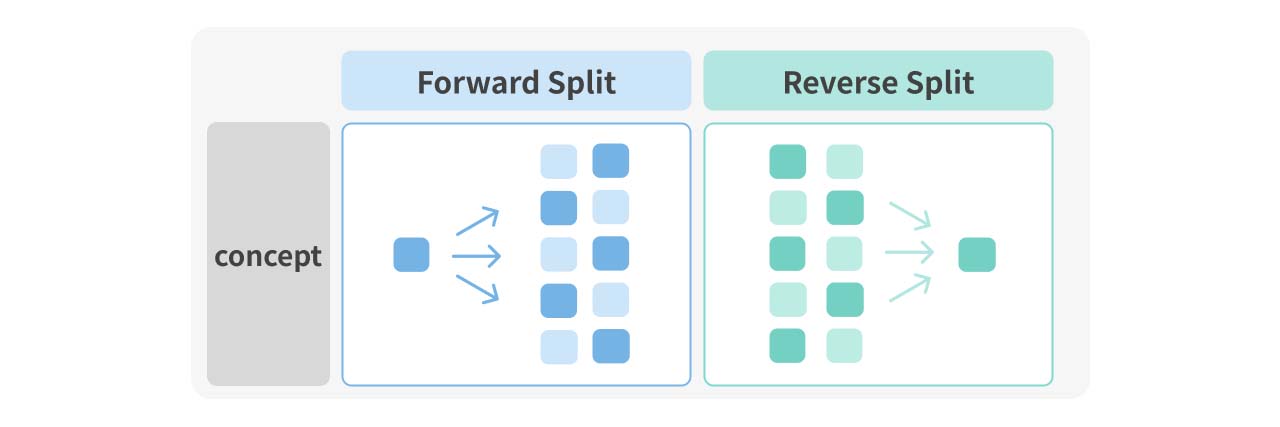
| Forward Split | Reverse Split | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Shares | Increase | Decrease |
| Stock Price | Decrease | Increase |
1. Forward Split
A forward split is the most common type of stock split, such as Nvidia's 1-for-10 plan (represented as 10-for-1 or 10:1 in U.S. markets). After a forward split, the total number of shares increases, while the price per share decreases. Forward splits are typically implemented when a company's stock price becomes too high. After the price decreases, the stock becomes more affordable for smaller investors, increasing liquidity and attracting more market participants.
2. Reverse Split
A reverse split, sometimes called as a stock consolidation, is the opposite of a forward split. For example, in a 1-for-2 reverse split (represented as 1-for-2 or 1:2 in U.S. markets), two original shares are consolidated into one, reducing the number of shares a shareholder holds, but increasing the price per share to maintain overall value. Reverse splits are often used to raise stock prices and avoid the risk of delisting due to low prices.
Reasons for Stock Splits
There are many reasons for stock splits, and the direction of the split often reflects different motivations. Here are the two main reasons for forward splits:
1. Increase Liquidity
As a stock’s price increases, liquidity tends to decrease. For small investors, stocks with high price may exceed their purchasing power. Even if they can buy a small number of shares, the high price limits their ability to diversify, as a large portion of their portfolio may be tied up in just a few stocks. These factors may deter some investors from participating.
2. Attract More Investors
By reducing the per-share price through a forward split, the stock becomes more accessible to a broader range of investors, addressing the concerns mentioned above. This is why stock splits are often said to capture the attention of retail investors.
Conclusion
Berkshire Hathaway Class A Shares (BRK.A)
However, some companies choose to maintain high share prices and refrain from splitting their stock, such as Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway Class A shares. You may notice that Berkshire Hathaway has both BRK.A and BRK.B share classes, with BRK.A currently priced at around $613,860. Warren Buffett believes that stock splits do not affect a company's intrinsic value, so he has resisted splitting Class A shares. Instead, the company issued lower-priced Class B shares to allow more investors to participate.
A stock split is a common corporate action primarily aimed at improving liquidity and market attractiveness. According to a Bank of America report analyzing past stock splits, companies that split their stock saw an average increase of 25% in share price within 12 months following the split. While stock splits do not change a company's total market capitalization or shareholders’ total holdings, they can have psychological effects on the market and influence investor behavior. Increased participation may heat up the market. Last but not least, as investors, it’s important to understand the meaning of stock splits and focus on a company’s long-term value growth for investment decisions.
